QUICK SUMMARY
Canadian fuel delivery companies face severe winter challenges as temperatures drop to −40°C, causing diesel gelling, equipment breakdowns, slower logistics, and unpredictable demand spikes. This quick guide highlights the most critical cold-weather obstacles and outlines proven solutions—from anti-gel treatments and winterized equipment to IoT sensors, predictive routing, and fuel delivery apps. Together, these strategies enable operators to maintain a safe and uninterrupted fuel supply during Canada’s harshest winter conditions.
On a harsh –40°C morning in Alberta, even the most experienced fuel delivery fleets face immediate pressure. Engines struggle to ignite, fuel lines begin to freeze, and planned routes quickly fall behind. For Canadian operators, winter isn’t just another season—it’s an intense operational challenge where every delivery must happen despite blizzards, icy roads, and equipment strain. Homes, businesses, and emergency services rely on an uninterrupted supply of heating oil and diesel.
To stay dependable, many providers now enhance traditional winter protocols with smart logistics tools and custom fuel delivery app development for safer, faster, cold-weather-ready operations.
Winter Fuel Demand in Canada: Key Statistics You Need to Know
- In January 2025, Canadian demand for natural gas rose 2.2% year over year, driven largely by colder temperatures in the residential and commercial sectors.
- In the same month, consumption of refined petroleum products (which includes distillate fuel oil, a key heating fuel) grew by 3.8% year over year.
- According to the Canadian Gas Association, during peak winter months (like January), peak natural gas demand can be more than 50% higher than the annual average monthly demand.
(Source: Canadian Gas Association: Peak demand facts and developments)
Understanding Winter Fuel Delivery Challenges in Canada
Canada’s Extreme Climate Conditions
Canada’s winter climate is one of the harshest in the world, creating an unforgiving environment for fuel delivery operations. Temperature extremes vary sharply across provinces—from –15°C averages in southern regions to –35°C and colder in northern territories. Many remote areas routinely experience –40°C wind chills, pushing both equipment and fuel systems beyond standard operating thresholds. Winter conditions also last 5–7 months, stretching from October through April, which means fuel distributors spend more than half the year operating in sub-zero environments with little margin for error.
The country’s massive geographic scale adds another layer of difficulty. Spanning 9.98 million square kilometers, Canada’s fuel delivery routes often cover long, remote stretches where infrastructure support is minimal. Reaching northern communities and industrial work sites can require hours of travel on partially maintained winter roads, especially during storms. These extended travel times increase fuel consumption, accelerate wear on vehicles, and heighten the risk of delays. Limited service stations, uneven road maintenance, and sparse emergency support further complicate winter logistics—making reliable fuel delivery both critical and challenging.
Canadian Provincial Winter Temperature Overview
| Province/Region | Average Winter Low (°C) | Extreme Cold Record (°C) | Winter Duration (Months) |
| British Columbia | –5 | –58 | 4 |
| Alberta | –15 | –61 | 5 |
| Saskatchewan | –20 | –57 | 5 |
| Manitoba | –23 | –53 | 5 |
| Ontario | –12 | –58 | 5 |
| Quebec | –15 | –45 | 4 |
| Atlantic Provinces | –10 | –47 | 5 |
| Territories | –30 | –63 | 7 |
Surging Winter Fuel Demand
Winter dramatically reshapes Canada’s energy consumption patterns. Residential customers rely heavily on heating oil, propane, and natural gas, causing 65–80% higher demand compared to summer months. Many homeowners begin stockpiling fuel as temperatures drop, resulting in sudden spikes in refill requests—especially during cold snaps and blizzards. Emergency top-ups become common when families underestimate their fuel needs or when long, cold stretches drive tanks lower than expected. For fuel providers, this seasonal surge creates sustained operational pressure to fulfill more orders in less predictable conditions.
Commercial and industrial sectors also experience elevated winter fuel requirements. Construction, manufacturing, logistics fleets, mining sites, and agricultural operations all depend on diesel-powered machinery that must run continuously despite freezing weather. Emergency services—hospitals, shelters, fire departments, and utility restoration teams—cannot afford interruptions and often receive priority fueling, especially during extreme cold or power outages. These high-stakes customers operate on a zero-tolerance policy for delivery failures, making reliability a core expectation for fuel distributors.
Critical Cold-Weather Challenges
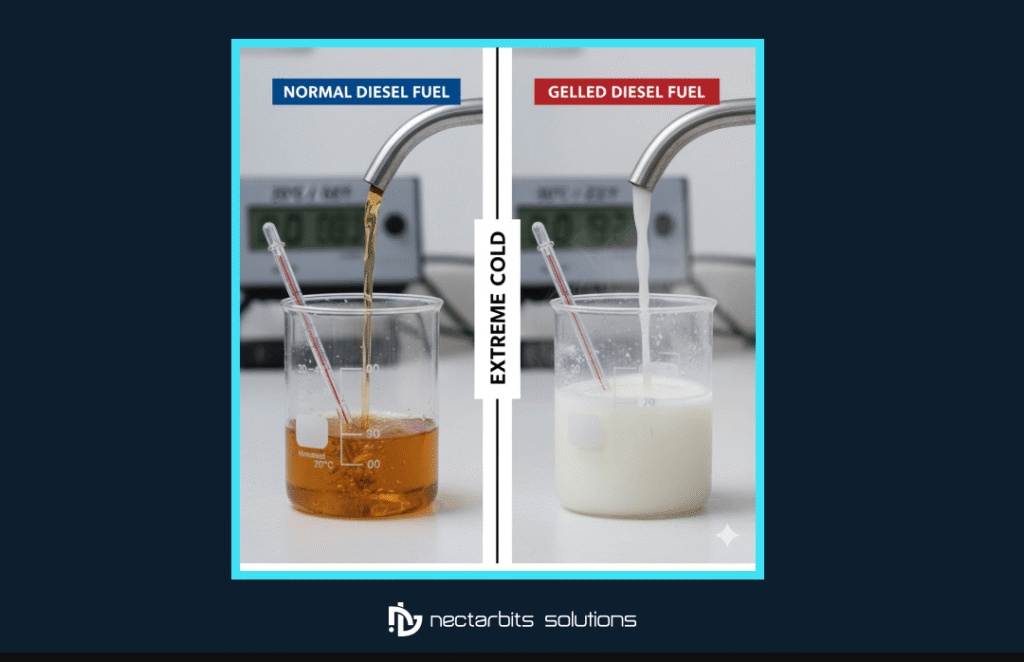
Cold weather directly impacts fuel behavior, creating significant operational risks. Diesel fuel begins to gel around –10°C, when paraffin wax crystallizes and thickens the liquid. As temperatures drop further, gelling accelerates; at –34°C, fuel can completely solidify, causing full blockages in tanks, filters, and delivery lines. This crystallization restricts fuel flow, clogs filters, and can stall engines mid-route—making fuel quality management one of winter’s biggest challenges. Even small temperature fluctuations can trigger waxing, especially in aging or untreated fuel.
Extreme cold also affects vehicle performance. Battery capacity can drop by up to 60% at –20°C, making engine starts more difficult and increasing the risk of roadside failures. Tire pressure decreases rapidly in frigid weather, hydraulic systems thicken or freeze, and onboard electronics may lag or fail. These mechanical vulnerabilities increase downtime and repair costs while posing serious safety risks for drivers navigating icy roads, whiteout blizzards, and remote regions where help may be hours away. For fuel delivery fleets, winter is a constant battle against both environmental and mechanical forces.
Specialized Strategies for Winter Operations
Canadian winters demand more than routine preparedness—they require operational precision, advanced technology adoption, and strict safety protocols. The following strategies outline how top-performing fuel delivery companies winterize their fleets, protect fuel quality, optimize routing, and safeguard drivers across some of the harshest conditions in the world.
Fleet Preparation and Winterization
Fleet winterization is the foundation of successful cold-weather fuel delivery. Without proper preparation, even the most advanced technology cannot compensate for frozen engines, battery failures, or clogged fuel systems.
1. Pre-Winter Mechanical Readiness (September–October)
A proactive inspection schedule ensures fleets are ready before the first major temperature drop.
- Full pre-winter vehicle inspection
- Battery load testing & proactive replacement cycles
- Switching to winter-grade oils and fluids
- Verifying tire condition, tread depth & pressure
- Testing cab heaters, defrosters & onboard HVAC systems
These early-season checks dramatically reduce roadside failures and help maintain service-level agreements during peak winter demand.
2. Daily Cold-Weather Maintenance Protocols
As temperatures drop, routine maintenance becomes essential.
- Block heater installation + mandatory plug-in protocols
- Warm indoor equipment staging to prevent cold starts
- Daily inspections for belts, hoses & visible frost damage
- Emergency kits stocked with blankets, flare markers, and traction aids
- Driver-first supplies like warm gear, hydration packs & food
Modern fleet managers rely on mobile app development services to automate maintenance reminders and track vehicle readiness—reducing downtime and preventing costly winter breakdowns.
3. Driver Support & Equipment Upgrades
Protecting drivers is just as important as protecting vehicles.
- Winter tires & optional chains for extreme routes
- Cold-weather PPE (thermal gloves, electric vests, insulated boots)
- Satellite phones or long-range radios for no-network regions
- First-aid kits designed for frostbite & hypothermia
- Portable power banks and backup lighting
These upgrades help fleets maintain safe operations even in remote northern communities.
Pre-Winter Vehicle Inspection Checklist
| System | Critical Checks | Priority | Est. Cost |
| Battery | Voltage test, age verification | Critical | $150–300 |
| Engine | Oil, coolant, belts, hoses | Critical | $200–500 |
| Fuel System | Lines, filters, additives | Critical | $100–400 |
| Tires | Tread depth, pressure, and chains | Critical | $800–2,000 |
| Heating | Block heater, cab heater | High | $150–600 |
| Safety Equipment | Emergency supplies, PPE | Critical | $300–700 |
Fuel Quality Management
Maintaining fuel quality during freezing temperatures is a science in itself. Poor fuel preparation is the #1 cause of winter service delays across Canada.
1. Winter Fuel Blending & Quality Control
Canadian suppliers adjust fuel formulations based on regional climate:
- Winter-grade blends optimized for northern provinces
- Coordination with suppliers to maintain seasonal inventory
- Frequent fuel sampling & lab testing
- Monitoring cloud point and pour-point levels
These steps ensure fuel remains flowable even in extreme cold.
2. Anti-Gel & Flow Improver Treatment Plans
Proper additive programs can prevent 90% of gelling incidents:
- Standard vs premium anti-gel usage
- Flow improvers for mid-range temperatures
- Emergency treatment solutions
- Automated dosing systems for consistency
3. Storage & Tank Protection Measures
Storage facilities must also be winter-ready:
- Weekly fuel testing during peak winter
- Heated storage tank systems
- Water contamination checks
- Temperature monitoring sensors for remote tanks
Fuel Additive Effectiveness Guide
| Additive Type | Temperature Range (°C) | Gel Point Reduction | Cost per 1000L | Best Use |
| Anti-gel Standard | 0 to -20 | -5 to -8°C | $8–12 | Regular ops |
| Premium Anti-gel | -10 to -35 | -10 to -15°C | $15–22 | Extreme cold |
| Flow Improver | -5 to -25 | -6 to -10°C | $10–16 | Moderate conditions |
| Winter Blend | 0 to -30 | -8 to -12°C | $5–8 | Seasonal |
| Emergency Treatment | -15 to -40 | -12 to -18°C | $25–40 | Already gelled |
Route Optimization and Technology
Smart routing becomes mission-critical when snowstorms, road closures, and black-ice conditions can disrupt operations within minutes.
1. Real-Time Weather-Aware Routing
Modern systems integrate:
- Live weather API feeds
- Automated route adjustments
- Road condition alerts
- Geo-specific storm forecasts
This enables dispatchers to anticipate disruptions—not simply react to them.
2. Priority Delivery & Critical Response Protocols
During peak winter demand:
- Hospitals, shelters & emergency services are prioritized
- Fleet load balancing prevents single-vehicle overload
- High-risk rural communities receive scheduled monitoring
- Customers receive automated delivery notifications
3. Backup Routing & Customer Communications
Strong contingency plans reduce operational downtime:
- Secondary and tertiary route planning
- Automated delay alerts for customers
- Real-time vehicle location sharing
- Resource reallocation to maintain service levels
An advanced fuel delivery app with real-time tracking enables accurate routing decisions even during blizzards.

Driver Training and Safety
Drivers face the most direct exposure to winter risks. A structured winter training program is essential.
1. Advanced Winter Driving Certifications
Training covers:
- Ice and snow handling
- Emergency recovery
- Skid control and braking
- Hazard recognition
2. Driver Wellness & Communication Protocols
- Mandatory check-ins before and after each run
- Health monitoring for cold stress symptoms
- Clear communication scripts for delays
- Structured incident reporting
3. Program Outcomes & Operational Impact
- Reduced winter accidents
- Faster delivery completion rates
- Increased driver confidence
- Lower insurance and maintenance expenses
Driver Training Program Components and Outcomes
| Training Component | Duration | Key Skills | Cost/Driver | ROI |
| Basic Winter Driving | 8 hrs | Ice/snow handling | $500 | 3:1 |
| Advanced Cold Weather | 12 hrs | Extreme conditions | $800 | 5:1 |
| Emergency Response | 6 hrs | First aid | $400 | 4:1 |
| Customer Communication | 4 hrs | Delay management | $200 | 2:1 |
| Health & Safety | 4 hrs | Cold stress, PPE | $300 | 6:1 |
Mobile Applications for Winter Logistics
Mobile technology has become the operational backbone of modern winter fuel delivery. Purpose-built mobile apps allow companies to stay connected, automate workflows, and keep drivers safe even in whiteout conditions.
1. Real-Time Communication & Emergency Safety Tools
Winter operations demand faster communication and smarter alert systems.
- Instant driver–dispatcher communication
- Voice-activated, hands-free controls for safer winter driving
- Automated severe weather alerts
- Built-in emergency SOS with GPS coordinates
- Two-way messaging for real-time updates
These capabilities reduce miscommunication, prevent delays, and improve driver safety when visibility and road conditions rapidly change.
2. Live Tracking, Customer Insights & Delivery Automation
Advanced mobile logistics apps ensure seamless coordination across customers, drivers, and dispatch.
- High-accuracy GPS tracking even in heavy snowfall
- Automated ETA notifications for customers
- Geofencing for accurate delivery confirmation
- Live map sharing for transparency
- Winter-route navigation with alternative snow-safe paths
3. Zero-Paper, Fully Digital Delivery Process
Mobile apps minimize outdoor exposure and streamline documentation.
- Electronic signature capture
- Photo documentation of tank conditions
- Automated fuel ticket generation
- Secure digital storage
- Direct integration with billing and ERP systems
Partnering with experienced Mobile App Development providers ensures these apps remain responsive, functional, and reliable even in extreme Canadian winter conditions.
IoT Sensors and Predictive Analytics
IoT is revolutionizing winter fuel delivery by eliminating guesswork. Sensors, automation, and AI-driven analytics help fleets monitor every critical metric—from tank levels to vehicle health—in real time.
1. Fuel Monitoring & Remote Diagnostics
IoT systems give operators unprecedented visibility.
- Fuel temperature sensors to prevent gelling
- Remote tank-level tracking with low-level alerts
- Real-time data transmission from remote sites
- Automated threshold warnings before issues arise
2. Vehicle Health Intelligence
Predictive maintenance dramatically reduces winter breakdowns.
- Battery voltage monitoring (critical in -20°C environments)
- Engine performance tracking
- Early fault detection
- Predictive maintenance alerts to schedule repairs before emergencies
3. Predictive Weather & Demand Analysis
AI-powered analytics turn winter uncertainty into predictable patterns.
- Weather forecasting linked to route changes
- Demand forecasting for high-usage weeks
- Automated resource allocation
- Intelligent maintenance scheduling based on environmental stress
An advanced IoT-enabled fuel logistics system connects vehicles, drivers, dispatchers, and customers, bringing full operational visibility to winter logistics.
Automated Dispatch Systems
AI-driven dispatch systems are becoming essential during Canada’s toughest winter months, where timing, fuel availability, and route accuracy directly impact safety and customer satisfaction.
1. AI-Powered Routing & Dynamic Adjustments
Automated dispatch engines continuously adapt to real-world winter challenges.
- AI-based route optimization
- Load balancing during peak weather disruptions
- Multi-stop efficiency calculations
- Real-time rerouting based on weather or accidents
- Fuel cost optimization through shorter & safer paths
2. Smart Scheduling & Workforce Automation
AI removes manual guesswork, improving reliability and reducing workload for dispatch teams.
- Predictive delivery scheduling
- Capacity planning algorithms
- Driver availability tracking
- Customer preference-based priority ranking
- Weather-informed resource allocation
These systems help companies maintain 24/7 uptime, improve delivery completion rates, and significantly reduce winter operational costs.

Emergency Preparedness and Risk Management
Winter operations in Canada demand a robust emergency framework. Fuel delivery companies must anticipate extreme weather events, supply interruptions, and operational breakdowns long before temperatures drop. A proactive emergency preparedness system—integrating contingency planning, financial risk mitigation, and technology-driven decision-making—is essential to ensure uninterrupted service even during severe cold snaps or blizzards.
Contingency Planning
Effective contingency planning ensures fuel delivery fleets remain operational despite unpredictable winter disruptions.
Companies typically secure backup supplier agreements to guarantee uninterrupted access to diesel, heating oil, and propane during peak shortages. Many also stage emergency fuel reserves near high-demand regions or remote communities, reducing delays caused by road closures or extended travel times. In extreme conditions, businesses may rely on alternative transportation arrangements, including tracked vehicles or contracted logistics partners. Priority is always given to critical customer segments—hospitals, shelters, industrial sites, and essential fleet operators.
Equally important are internal and customer-facing communication systems. Automated alert platforms notify customers of delays, route changes, or emergency advisories. Companies must also comply with regional safety and regulatory reporting requirements, especially during fuel shortages or severe weather alerts. A strong crisis communication protocol guides staff on escalation procedures, while internal coordination ensures dispatchers, drivers, technicians, and management act in sync during emergencies.
Looking to strengthen your cost strategy? Explore our detailed guide on fuel delivery app development
Financial Risk Management
Managing winter-related financial risks is essential for profitability and operational continuity. Leading Canadian fuel delivery companies invest in weather-related insurance coverage, protecting assets from storm damage, accidents, and freezing incidents. They also implement fuel cost fluctuation strategies, such as hedging and bulk purchasing, to stabilize expenses when demand spikes. Emergency service pricing models create transparent expectations for customers while enabling sustainable margins during high-risk periods. Many operators allocate dedicated winter budgets for equipment winterization, staff overtime, and vehicle reinforcement.
Winter maintenance isn’t an expense—it’s an investment. A well-maintained fleet reduces breakdown probability, delivering strong ROI through fewer repairs and reduced downtime. Technology systems such as IoT sensors, real-time monitoring, and automated dispatch offer long-term savings by optimizing fuel usage and lowering operational errors. Companies that invest early gain a competitive edge through higher reliability, better customer trust, and improved service continuity.
Emergency Response Protocol Checklist
| Scenario | Immediate Action | Communication Plan | Backup Resources | Recovery Time |
| Extreme cold snap (-40°C+) | Activate emergency protocols | Alert all customers | Deploy reserve vehicles | 2–4 hours |
| Heavy snowfall (30cm+) | Reroute deliveries | Update ETAs | Coordinate with snowplows | 4–8 hours |
| Vehicle breakdown | Dispatch backup truck | Notify affected customers | Mobile repair unit | 1–3 hours |
| Driver safety issue | Immediate extraction | Contact emergency services | Deploy a relief driver | 30–60 min |
| Fuel quality problem | Halt deliveries | Issue quality alert | Source replacement fuel | 6–12 hours |
Case Study Snapshot
A mid-sized Alberta fuel delivery company faced severe performance issues during a winter season with temperatures dropping to –35°C. Nearly 40% of deliveries were delayed or failed, mainly due to frozen lines, limited visibility, and communication gaps. To stabilize operations, the company adopted a custom mobile delivery app, installed IoT temperature and fuel-level sensors, and upgraded its driver winter training program. Within one season, the company achieved 89% on-time delivery, a 71% reduction in incidents, and a 34% efficiency improvement across routes.
Key Lessons Learned
- Early preparation significantly reduces emergencies
- Technology-driven monitoring boosts reliability
- Driver training offers one of the highest winter ROI
- Strong customer communication minimizes complaints and churn
Future Trends in Winter Fuel Delivery
As Canada’s winters become increasingly unpredictable, the fuel delivery industry is rapidly transforming through next-generation technologies, sustainability frameworks, and smarter logistics models. Future-ready companies are investing in automation, AI-driven weather intelligence, and greener fuel alternatives to enhance reliability in cold climates. These trends are shaping the next decade of winter fuel delivery. improving safety, reducing operational costs, and strengthening environmental performance across the country. For emerging businesses, early technology adoption and strong digital foundations. such as MVP development for fuel delivery startup models, are becoming essential for long-term competitiveness.
Emerging Technologies
The future of winter fuel delivery is increasingly powered by innovation. Electric delivery vehicles (EVs) are undergoing cold-weather adaptations, including heated battery enclosures and improved thermal management to prevent rapid charge loss in sub-zero temperatures. Companies are integrating AI-based weather prediction systems, enabling real-time route adjustments and proactive risk prevention. As autonomy advances, self-driving delivery trucks may support low-visibility or high-risk routes, while improvements in battery density and freezing-resistant chemistries boost winter performance.
Cold-climate operations will also benefit from alternative fuels such as renewable diesel, biofuels, and hydrogen blends, which retain stability in winter conditions. Blockchain solutions are emerging to ensure supply chain transparency, prevent fraud, and verify fuel quality at every transfer point. For extremely remote northern regions, drone-based micro-deliveries may assist in urgent refills or sample testing. Meanwhile, advanced composite materials in hoses, tanks, and pumps increase durability against deep-freeze stress.
Sustainability in Winter Operations
Sustainable winter fuel delivery is quickly becoming a competitive advantage. Companies are adopting eco-friendly winter operations, including idling-reduction policies, low-emission fleet upgrades, and optimized routing to cut unnecessary mileage. To reduce environmental impact, providers are gradually shifting toward green fuel alternatives that perform reliably in sub-zero climates, such as renewable diesel and clean-burning propane. Additionally, energy-efficient heating systems and insulated storage help maintain fuel quality without excessive energy consumption.
Regulatory expectations are also rising. Provinces increasingly require carbon reporting, clean-fuel compliance, and climate-risk disclosures from logistics companies. Industry-wide sustainability initiatives—like cleaner fleet certification and winter efficiency benchmarking—are pushing operators toward higher standards. Organizations focusing on long-term viability strategies such as emissions monitoring, green fleet planning, and circular-waste reduction will be best positioned to thrive in Canada’s cold future.
Want to explore digital solutions that support sustainability? Check out our guide on: custom fuel delivery app development with agile methodology and 70% ROI increase
Conclusion: Thriving in Canadian Winters
Canadian winters demand more than routine operations—they require strong preparation, the right technology, and trained teams. Companies that invest early in winter readiness gain reliability, customer trust, and a real competitive edge.
Start gearing up before temperatures drop. Plan upgrades, integrate tech systems, and train teams by September–October to ensure smooth operations all season.
The future of fuel delivery in Canada will be shaped by innovation. With rising customer expectations, winter-ready systems will become the true differentiator for leading fuel delivery companies.

Frequently Asked Questions:
1. How do fuel delivery companies prevent diesel from gelling in extreme Canadian winters?
Fuel providers use winterized diesel blends, premium anti-gel additives, heated storage systems, and IoT-enabled fuel temperature monitoring. These measures ensure fuel stays flowable even at –30°C to –40°C.
2. What technologies help improve fuel delivery reliability during winter storms?
AI-powered routing, real-time weather data integration, mobile apps with live tracking, and IoT sensors (for tank levels, engine health, and temperature) drastically reduce delays, breakdowns, and missed deliveries during harsh weather.
3. When should fleets start preparing for winter operations in Canada?
Most fleets begin winterization in September–October, covering inspections, tire changes, additive planning, driver training, and technology upgrades. Early preparation prevents unexpected breakdowns once temperatures drop below –20°C.
4. How can fuel delivery companies maintain customer satisfaction during severe weather delays?
Companies rely on automated ETA updates, customer communication apps, priority batching for critical clients, transparent delay notifications, and backup routing plans. This reduces complaints and keeps customers informed during disruptions.




