The fuel delivery industry operates under some of the strictest regulatory frameworks in the commercial sector—and for good reason. With over 254 million vehicles on U.S. roads alone (Federal Highway Administration, 2023), the demand for safe, compliant fuel delivery has never been higher. Yet, navigating the complex web of compliance requirements remains one of the biggest challenges for fuel delivery businesses.
According to the U.S. Department of Transportation, non-compliance incidents in hazardous materials transportation resulted in over $8.2 million in penalties in 2024 alone. For fuel delivery companies, regulatory risk isn’t just high—compliance is absolutely non-negotiable.
Whether you’re launching a new fuel delivery service or optimizing an existing operation, understanding and implementing proper safety regulations can mean the difference between thriving success and costly shutdowns. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about fuel delivery compliance and safety regulations in 2025.
Understanding the Regulatory Landscape of Fuel Delivery
Why Fuel Delivery Compliance Matters More Than Ever
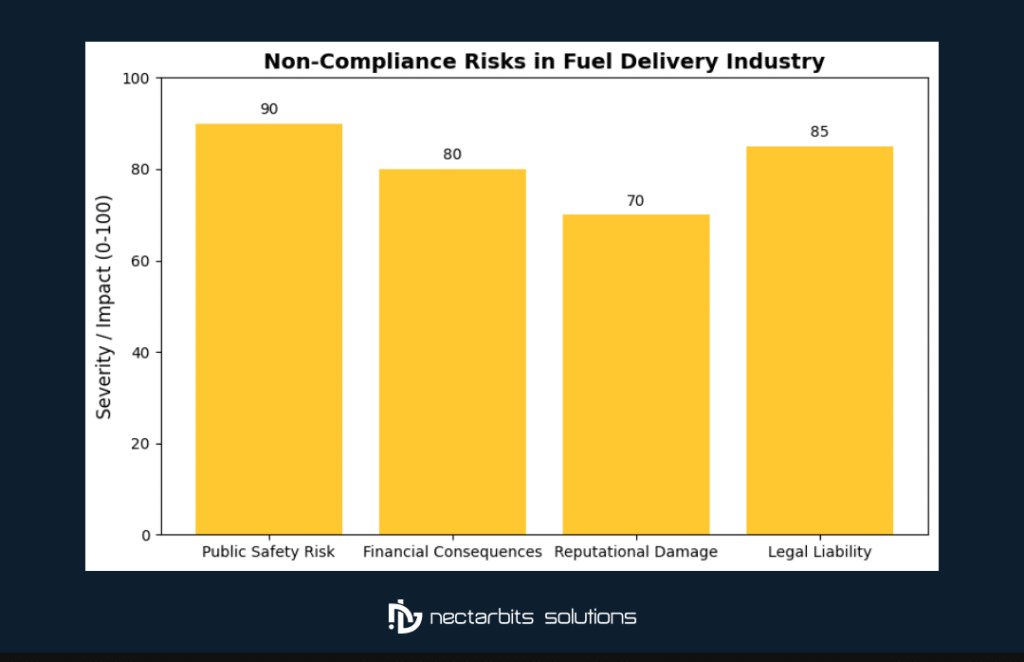
Fuel delivery compliance isn’t just about avoiding fines—it’s about protecting lives, preserving the environment, and building sustainable business operations. The fuel delivery industry faces unique challenges:
- Public Safety Risk: A single compliance failure can result in catastrophic accidents, environmental disasters, and loss of life
- Financial Consequences: Non-compliance penalties can reach $75,000 per violation per day
- Reputational Damage: Safety incidents can permanently damage brand trust and customer relationships
- Legal Liability: Companies face criminal charges and civil lawsuits for serious violations
According to National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) data, proper compliance with fuel handling regulations reduces incident rates by up to 68%.
Key Regulatory Bodies Governing Fuel Delivery
Multiple agencies oversee different aspects of fuel delivery compliance:
| Regulatory Agency | Jurisdiction | Primary Focus |
| DOT (Department of Transportation) | Federal/State | Vehicle safety, driver qualifications, transportation standards |
| EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) | Federal | Worker safety, training requirements, and workplace hazards |
| OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) | Federal | Worker safety, training requirements, workplace hazards |
| PHMSA (Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration) | Federal | Hazmat transportation, packaging, labeling |
| State Environmental Agencies | State | Local environmental regulations, permitting |
| Fire Marshal Offices | Local | Fire safety codes, storage regulations |
Understanding which regulations apply to your specific operation is the first step toward comprehensive compliance.

Essential Fuel Delivery Safety Regulations You Must Follow
1. Hazardous Materials Transportation Standards (49 CFR)
The Code of Federal Regulations Title 49 governs the transportation of hazardous materials, including fuel:
Key Requirements:
- Proper vehicle placarding and labeling
- Hazmat endorsement for commercial drivers
- Emergency response information during transport
- Shipping paper documentation
- Vehicle inspection protocols
Compliance Impact: Violations of 49 CFR can result in $500-$75,000 per violation, with criminal penalties for serious infractions.
2. DOT Driver Qualification Standards
Fuel delivery drivers must meet stringent qualification requirements:
- Commercial Driver’s License (CDL) with Hazmat endorsement
- Medical certification (renewed every 2 years)
- Background checks, including drug and alcohol screening
- Training documentation for hazmat handling
- Hours of service compliance to prevent fatigue
According to the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration, proper driver qualification reduces accident rates by 43%.
3. Environmental Protection Regulations
Environmental compliance is critical for fuel delivery operations:
Spill Prevention, Control, and Countermeasure (SPCC) Plans:
- Required for facilities storing more than 1,320 gallons of oil
- Must include containment procedures and emergency response protocols
- Regular updates and employee training mandatory
Clean Air Act Compliance:
- Vapor recovery systems during fuel transfer
- Emissions monitoring and reporting
- Vehicle emissions standards compliance
Statistics: The EPA reported that proper SPCC plan implementation reduces environmental incidents by 72% (EPA Environmental Compliance Report).
4. Occupational Safety Standards (OSHA)
Worker safety regulations protect fuel delivery personnel:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) requirements
- Confined space entry protocols
- Fire safety and prevention training
- Hazard communication standards
- Emergency action plans
Companies with comprehensive OSHA compliance programs experience 52% fewer workplace injuries
Technology Solutions for Maintaining Fuel Delivery Compliance
How Digital Solutions Streamline Compliance Management
Modern technology has revolutionized how fuel delivery companies manage compliance. A robust fuel delivery app development solution can automate many compliance tasks:
Automated Compliance Features:
- Real-time driver credential verification
- Automated hours of service tracking
- Digital inspection checklists and documentation
- GPS tracking for route compliance
- Automated regulatory reporting
- Digital training and certification management
Compliance Dashboard Benefits:
| Traditional Method | Digital Solution | Time Saved |
| Manual inspection logs | Automated digital checklists | 67% |
| Paper-based training records | Cloud-based certification tracking | 73% |
| Manual route planning | AI-optimized compliance routing | 58% |
| Physical document storage | Digital document management | 81% |
Real-Time Monitoring and Alert Systems
A sophisticated SaaS based fuel delivery app solution enables:
- Instant violation alerts when compliance thresholds are approached
- Predictive maintenance scheduling to prevent equipment failures
- Automatic documentation of all delivery activities
- Geofencing capabilities to enforce restricted zone compliance
- Temperature and pressure monitoring during transport
According to Fleet Management Technology Reports, companies using digital compliance solutions reduce violations by 64% (Fleet Technology Insights).
Integration with Regulatory Reporting Systems
Custom software development solutions can integrate directly with regulatory agencies:
- Automated IFTA reporting (International Fuel Tax Agreement)
- Electronic logging device (ELD) compliance
- Direct submission to DOT databases
- Environmental reporting automation
- Incident reporting workflows

Building a Comprehensive Compliance Program
Step 1: Conduct a Compliance Audit
Start with a thorough assessment of your current compliance status:
Audit Checklist:
- Review all applicable federal, state, and local regulations
- Assess current driver qualifications and training
- Evaluate vehicle inspection and maintenance records
- Review environmental compliance documentation
- Examine emergency response procedures
- Analyze incident and violation history
Pro Tip: Companies that conduct quarterly compliance audits identify 89% of potential violations before they occur (Compliance Best Practices Study).
Step 2: Develop Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
Create detailed, written procedures for all compliance-critical operations:
Essential SOPs Include:
- Pre-delivery vehicle inspection protocol
- Fuel transfer safety procedures
- Spill response and containment steps
- Driver safety and emergency protocols
- Equipment maintenance schedules
- Documentation and record-keeping procedures

Step 3: Implement Comprehensive Training Programs
Ongoing training is essential for maintaining fuel delivery compliance. A structured program ensures that drivers and staff are fully prepared to handle regulatory and safety requirements.
Initial Onboarding (Week 1–2):
During the first weeks, personnel receive training on regulatory overviews and company policies, hazmat handling and transportation, emergency response procedures, and equipment operation and safety.
Ongoing Training (Quarterly):
Quarterly sessions focus on regulation updates, incident reviews and lessons learned, refresher courses on critical procedures, and training on new technology and tools.
Annual Certification:
Personnel undergo hazmat recertification, safety protocol updates, compliance testing and evaluation, and performance reviews to maintain high standards.
Companies with structured training programs report 76% fewer compliance violations.
Step 4: Establish Monitoring and Accountability Systems
Create systems to ensure ongoing compliance:
- Regular compliance meetings with leadership
- Key performance indicators (KPIs) for safety metrics
- Accountability structures for compliance failures
- Incentive programs for safety excellence
- Third-party compliance audits annually
Common Compliance Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Challenge 1: Keeping Up with Changing Regulations
The Problem: Fuel delivery regulations are constantly evolving. The DOT alone publishes over 200 regulatory updates annually.
The Solution:
- Subscribe to regulatory update services
- Assign a compliance officer to monitor changes
- Implement agile technology systems that can quickly adapt
- Partner with compliance consultants
- Use custom software development solutions with automatic regulation updates
Challenge 2: Managing Driver Compliance
The Problem: Ensuring all drivers maintain proper qualifications, certifications, and comply with hours of service regulations.
The Solution:
- Automated credential tracking systems
- Digital driver qualification files
- Real-time hours of service monitoring
- Mobile apps for driver self-service
- Automated expiration alerts and renewal reminders
When you hire dedicated developers for fuel delivery apps, you can create custom solutions that address your specific driver management challenges.
Challenge 3: Documentation and Record-Keeping
The Problem: Fuel delivery compliance requires extensive documentation. The average fuel delivery company maintains over 15,000 compliance documents annually.
The Solution:
- Cloud-based document management systems
- Automated data capture and storage
- Digital signature capabilities
- Searchable, indexed databases
- Automated backup and archival systems
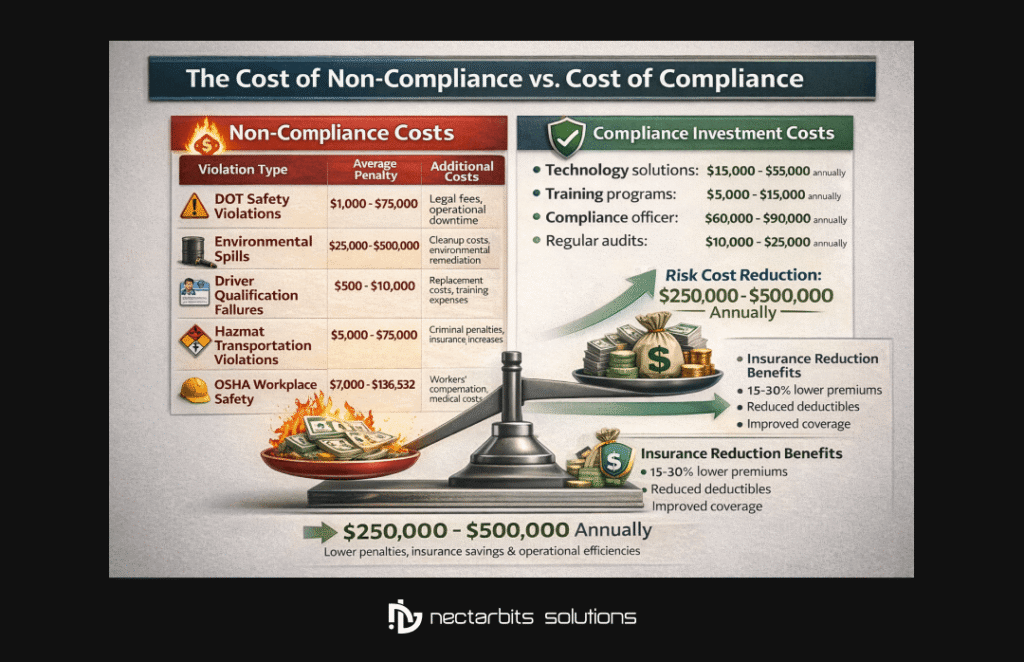
The Financial Impact of Compliance
Cost of Non-Compliance vs. Cost of Compliance
Understanding the financial implications helps justify compliance investments:
Non-Compliance Costs:
| Violation Type | Average Penalty | Additional Costs |
| DOT Safety Violations | $1,000 – $75,000 | Legal fees, operational downtime |
| Environmental Spills | $25,000 – $500,000 | Cleanup costs, environmental remediation |
| Driver Qualification Failures | $500 – $10,000 | Replacement costs, training expenses |
| Hazmat Transportation Violations | $5,000 – $75,000 | Criminal penalties, insurance increases |
| OSHA Workplace Safety | $7,000 – $136,532 | Workers’ compensation, medical costs |
Compliance Investment Costs:
- Technology solutions: $15,000 – $50,000 annually
- Training programs: $5,000 – $15,000 annually
- Compliance officer: $60,000 – $90,000 annually
- Regular audits: $10,000 – $25,000 annually
ROI Analysis: Companies investing in comprehensive compliance programs reduce total risk costs by an average of $250,000 – $500,000 annually.
Insurance Benefits of Strong Compliance
Insurers reward fuel delivery compliance:
- Premium reductions of 15-30% for exemplary safety records
- Lower deductibles for companies with compliance programs
- Better coverage terms and expanded protection
- Faster claims processing with documented compliance
Industry Best Practices for Fuel Delivery Safety Regulations
1. Adopt a Safety-First Culture
The most compliant companies embed safety into their organizational DNA:
- Leadership commitment to safety over profits
- Open communication about safety concerns
- No-blame reporting for near-miss incidents
- Recognition programs for safety excellence
- Continuous improvement mindset
2. Leverage Predictive Analytics
Advanced analytics can predict compliance risks before they occur:
- Driver behavior analysis to identify high-risk patterns
- Equipment failure prediction through sensor data
- Route optimization for safety and compliance
- Incident trend analysis for preventive action
3. Maintain Crisis-Ready Operations
Compliance includes being prepared for emergencies. See how on-demand fuel apps ensured safety and uptime in lockdowns for crisis management insights.
Crisis Preparedness Checklist:
- Updated emergency response plans
- 24/7 incident response team
- Regular emergency drills
- Backup communication systems
- Supplier and contractor emergency contacts
- Public relations crisis protocols
4. Implement Continuous Improvement Processes
Top-performing companies never stop improving:
- Monthly safety committee meetings
- Quarterly compliance reviews
- Annual third-party audits
- Benchmarking against industry leaders
- Technology upgrades and modernization
Future Trends in Fuel Delivery Compliance
Emerging Technologies Shaping Compliance
The future of fuel delivery compliance is increasingly digital:
Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning:
- Predictive compliance risk scoring
- Automated violation detection
- Intelligent route optimization for safety
Internet of Things (IoT):
- Real-time tank monitoring
- Automated leak detection
- Vehicle telematics integration
Blockchain Technology:
- Immutable compliance records
- Smart contracts for automated compliance
- Transparent supply chain tracking
Autonomous Vehicles:
- Elimination of driver qualification issues
- Consistent safety protocol execution
- Reduced human error incidents
According to McKinsey & Company, companies adopting AI-powered compliance solutions reduce compliance costs by 40% while improving adherence by 35% (McKinsey Digital Compliance Report).
Evolving Regulatory Requirements
Stay ahead of anticipated regulatory changes:
- Stricter emissions standards for delivery vehicles
- Enhanced cybersecurity requirements for digital systems
- Increased transparency in supply chain tracking
- Higher penalties for repeat violations
- Expanded environmental protection mandates
Your Compliance Action Plan: Next Steps
30-Day Compliance Quick-Start Guide
Week 1: Assessment
- Conduct initial compliance audit
- Identify critical gaps and violations
- Prioritize high-risk areas
Week 2: Planning
- Develop a compliance improvement roadmap
- Assign responsibilities and resources
- Set measurable compliance goals
Week 3: Implementation
- Begin driver training programs
- Implement technology solutions
- Update SOPs and documentation
Week 4: Monitoring
- Establish KPI tracking
- Create reporting dashboards
- Schedule ongoing compliance reviews
Building Your Technology Infrastructure
Modern fuel delivery compliance requires robust technology. A comprehensive fuel delivery app development solution provides:
- Centralized compliance dashboard
- Automated documentation and reporting
- Real-time monitoring and alerts
- Integration with regulatory databases
- Mobile accessibility for drivers and managers

Conclusion: Compliance is Your Competitive Advantage
Fuel delivery compliance and safety regulations aren’t just legal obligations—they’re the foundation of sustainable, profitable fuel delivery operations. Companies that excel at compliance enjoy:
- Reduced operational costs through fewer violations and incidents
- Enhanced reputation and customer trust
- Lower insurance premiums and better coverage
- Competitive advantages in securing contracts
- Long-term business sustainability
In an industry where regulatory risk is high and compliance is non-negotiable, investing in comprehensive compliance programs isn’t optional—it’s essential for survival and growth.
The complexity of fuel delivery safety regulations may seem daunting, but with the right strategies, technology, and commitment to excellence, your company can not only meet compliance requirements but exceed them, building a safer, more profitable future
Related Reading
Want to dive deeper into fuel delivery safety and technology?
Discover how leading fuel delivery companies are leveraging technology to enhance safety, build customer trust, and maintain flawless compliance records. Learn more about building trust through safety-first fuel delivery app design and explore best practices that separate industry leaders from the rest.
FAQs:-
Q1: What are the most critical fuel delivery compliance regulations my fleet must follow?
Key regulations include DOT Hazmat standards, EPA environmental rules, OSHA safety standards, and local fire codes. Driver qualifications, labeling, spill prevention, and training are essential.
Q2: How can technology help my fuel delivery business maintain compliance
Fuel delivery apps automate driver checks, GPS tracking, digital inspections, alerts, and reporting, reducing violations and saving time.
Q3: What are common compliance challenges in fuel delivery, and how do I overcome them?
Challenges include changing regulations, driver compliance, and record-keeping. Solutions: automated tracking, cloud documents, and regular training.
Q4: What financial benefits can a compliant fuel delivery operation provide?
Compliance reduces fines, insurance costs, and risks, saving $250k–$500k yearly and improving business credibility.