Route planning represents the single largest controllable cost variable in fuel delivery operations. With fuel costs rising 23% year-over-year and labor expenses up 15%, inefficient routing directly threatens business survival. According to the American Transportation Research Institute (ATRI), trucking operating costs have risen significantly, compressing profit margins to just 3–8%, leaving virtually no room for operational waste
Yet most fuel delivery operators still rely on manual planning, basic GPS navigation, or outdated routing systems—leaving 25-40% operational efficiency on the table.
Fuel delivery route optimization is no longer a competitive advantage—it’s a survival necessity. Companies implementing advanced delivery route planning software achieve 30-40% cost reductions, 25-35% more deliveries per vehicle, and 18-22% fuel savings within the first year, according to the American Transportation Research Institute.
This comprehensive guide reveals proven best practices, essential technologies, and actionable implementation strategies that deliver measurable results within weeks, not months.
Understanding Fuel Delivery Route Optimization
What Makes Fuel Delivery Routing Unique
Unlike package delivery or general logistics, fuel delivery presents distinct routing challenges that require specialized optimization approaches.
Unique Fuel Delivery Constraints:
| Challenge | Impact on Routing | Optimization Requirement |
| Variable Delivery Volumes | Trucks don’t carry uniform “packages.” | Must calculate capacity vs. demand precisely |
| Multi-Compartment Loads | Gasoline, diesel, and biofuels can’t mix | Compartment-level sequencing required |
| Hazmat Regulations | Route restrictions, tunnel prohibitions | Compliance-based routing required |
| Time-Sensitive Deliveries | Commercial fleets can’t run out | Emergency insertion capability is essential |
| Tank Access Constraints | Physical space, delivery hours | Site-specific routing parameters |
| Return-to-Base Requirements | Can’t end the route anywhere | Circular routing optimization |
The True Cost of Suboptimal Routing
According to Geotab Fleet Benchmarking Data, fuel delivery operations using manual or basic routing experience:
- 28-35% excess mileage compared to optimal routes
- 12-18 wasted miles per vehicle per day (10-vehicle fleet = 120-180 miles daily waste)
- 22-30 minutes lost time per delivery due to poor sequencing
- 15-25% underutilized capacity (trucks not optimally loaded)
- $47,000-$125,000 annual waste for medium-sized operations
Cost Impact Analysis – 10 Vehicle Fleet:
| Cost Factor | Optimal Routing | Suboptimal Routing | Annual Waste |
| Daily Miles | 1,800 | 2,340 (+30%) | – |
| Fuel Cost (@$3.85/gal, 7 MPG) | $358,800 | $466,440 | $107,640 |
| Labor Cost (@$28/hr loaded) | $616,720 | $740,064 | $123,344 |
| Maintenance (@$0.15/mile) | $98,550 | $128,115 | $29,565 |
| Vehicle Depreciation | $120,000 | $144,000 | $24,000 |
| TOTAL DIRECT COST WASTE | – | – | $284,549/year |
Beyond cost waste, suboptimal routing limits delivery capacity by 17-25%, forcing fleet expansion investment or declining growth opportunities worth $150,000-$350,000 in annual lost revenue.

Best Practice 1: Multi-Variable Dynamic Optimization
Beyond Simple Point-to-Point Navigation
Effective fuel delivery route optimization requires simultaneous optimization of dozens of variables rather than simple distance calculations.
Critical Optimization Variables:
| Variable Category | Specific Factors | Optimization Impact |
| Geographic | Distance, traffic patterns, road types, and elevation | 25-35% mileage reduction |
| Temporal | Delivery windows, driver shifts, traffic timing | 18-25% time savings |
| Capacity | Tank compartments, product mix, volumes | 20-30% more deliveries/vehicle |
| Regulatory | Hazmat routes, weight restrictions, and prohibitions | Compliance + efficiency |
| Customer | Access hours, site constraints, service levels | Satisfaction + efficiency |
| Fleet | Vehicle type, maintenance, fuel efficiency | 12-18% cost reduction |
Sequential vs. Simultaneous Optimization
Traditional Sequential Approach (Suboptimal):
- Assign orders to vehicles based on geography
- Sequence stops by proximity
- Calculate routes between stops
- Adjust for time windows
Result: Locally optimal decisions create globally suboptimal routes
Advanced Simultaneous Optimization:
- All variables are considered concurrently in a single process
- Machine learning identifies patterns humans miss
- Constraint satisfaction algorithms balance competing priorities
Performance Comparison:
| Metric | Sequential | Simultaneous | Improvement |
| Total Route Miles | 2,145 | 1,620 | -24% |
| Deliveries Completed | $132 | $168 | $0 |
| Route Planning Time | 45 minutes | 3 minutes | -93% |
| On-Time Performance | 87% | 96% | $0 |
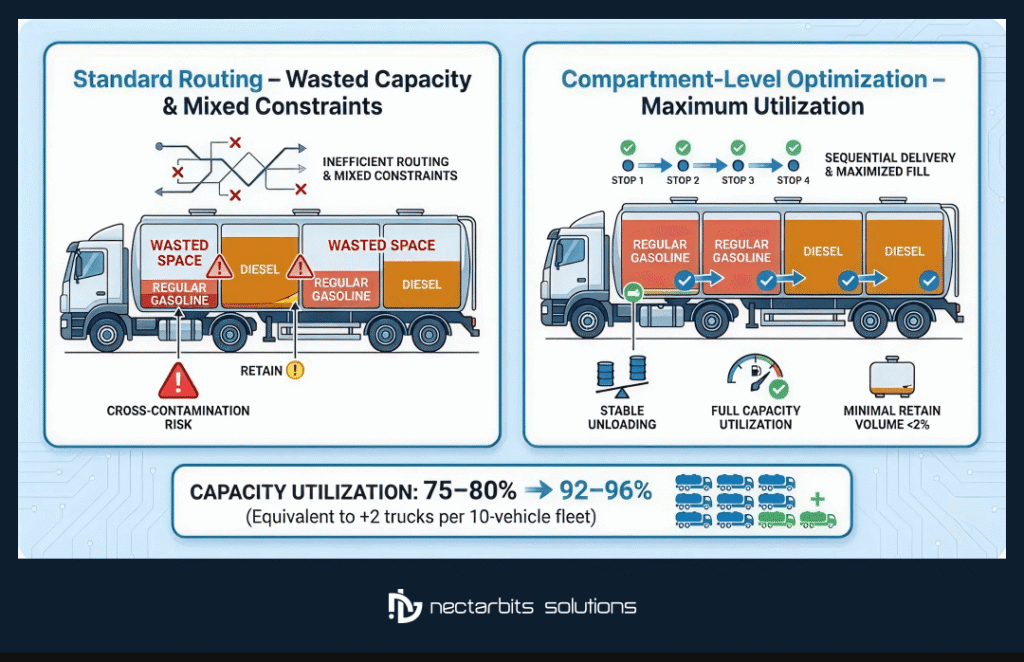
Best Practice 2: Compartment-Level Load Optimization
Solving the “Tetris” Problem of Fuel Delivery
Standard routing software fails in fuel delivery because it treats a truck as a single box. Fuel trucks are compartmentalized (often 3-5 separate tanks), carrying different grades that cannot mix.
The Multi-Compartment Challenge:
- Cross-Contamination: Cannot put Diesel in a compartment that holds Gasoline without flushing
- Split Drops: A single customer might need 500 gallons of Diesel + 200 gallonsof Regular
- Retains: Returning to base with 100 gallons left in a 2,000-gallon compartment wastes capacity
The Optimization Solution:
Advanced algorithms from a Fuel delivery app development company perform “Load Balancing” simultaneously with route planning:
- Optimal Loading: Which product goes in which compartment to match the route sequence
- Discharge Sequence: Ensures the truck unloads to maintain vehicle stability (preventing sloshing)
- Return Minimization: Plans routes ensuring truck returns near empty (<2% retain)
Impact: Proper compartment optimization increases effective capacity utilization from 75-80% to 92-96%—equivalent to adding 2 vehicles to a 10-vehicle fleet without purchasing trucks.
Best Practice 3: Real-Time Dynamic Rerouting
Static Routes in Dynamic Environments
Traditional route planning creates static daily routes that become obsolete when real-world conditions change.
Dynamic Factors Requiring Rerouting:
- Traffic incidents: Accidents, construction, congestion
- Weather conditions: Snow, rain, flooding
- Vehicle issues: Breakdowns, maintenance needs
- Customer changes: Cancellations, urgent additions
- Driver situations: Delays, early completions
Impact of Static Routing:
- 18-25% of planned routes encounter significant disruptions daily
- 65-90 minutes average lost time per disrupted route
- $45-$85 daily cost per affected vehicle
Real-Time Optimization Capabilities
Advanced delivery route planning software provides continuous optimization:
| Capability | How It Works | Business Impact |
| Live Traffic Integration | Updates routes every 3-5 minutes | Avoid delays, maintain schedules |
| Predictive Traffic Analysis | ML predicts congestion before it appears | Proactive routing adjustments |
| Dynamic Order Insertion | Urgent orders inserted with minimal disruption | Emergency service without chaos |
| Automatic Resequencing | Route order adjusts based on actual progress | Optimize throughout the day |
| Driver Communication | Route changes are pushed instantly to driver apps | No phone calls, instant adaptation |
Results: 22% reduction in weather-related delays, 31% improvement in on-time delivery, $32,000 annual savings per 10 vehicles.
Best Practice 4: Predictive Analytics and Machine Learning
Learning from Historical Data
Fuel delivery route optimization powered by machine learning improves continuously:
1. Consumption Pattern Forecasting
- Predicts when customers need refills (±2-3 days accuracy)
- Enables proactive route planning
- Impact: 18-25% reduction in reactive deliveries
2. Traffic Pattern Prediction
- Predicts traffic conditions 24-72 hours ahead
- Enables optimal delivery time scheduling
- Impact: 12-18% reduction in traffic-related delays
3. Delivery Time Estimation
- Predicts actual delivery duration (±5 minutes accuracy)
- Enables realistic scheduling
- Impact: 96%+ on-time performance vs. industry average 82%
Machine Learning Evolution:
| Time Period | Optimization Accuracy | Cost Efficiency |
| Week 1 | Baseline | Baseline |
| Month 1 | +15% improvement | +15% savings |
| Month 3 | +28% improvement | +28% savings |
| Month 12 | +42% improvement | +42% savings |
Essential Technologies for Route Optimization
Component 1: Advanced Routing Engine
A specialized Fuel delivery app development company builds routing engines with:
Algorithm Requirements:
| Algorithm Type | Application | Performance |
| Capacitated VRP | Volume/compartment constraints | Multi-product deliveries |
| VRP with Time Windows | Customer time window compliance | 95%+ window adherence |
| Dynamic VRP | Real-time rerouting | Sub-3-minute recalculation |
| Machine Learning Enhanced | Continuous improvement | 35-45% better than basic VRP |
Component 2: Mobile Driver Applications with Offline Capability
Route plans only work if drivers can execute them. Mobile app development solutions must include:
Essential Features:
| Feature | Function | Efficiency Impact |
| Turn-by-Turn Navigation | GPS routing with voice guidance | Eliminate wrong turns |
| Stop Sequencing | Optimized delivery order | No decision paralysis |
| Proof of Delivery | Digital signature, photo capture | Reduce paperwork time |
| Real-Time Updates | Dynamic route changes pushed live | Adapt to changes instantly |
Critical: Offline-First Architecture
Fuel delivery often takes drivers to “dead zones”—rural farms, construction sites, and underground docks where cellular signals fail.
The “Sync-Later” Solution:
- The entire day’s route was downloaded to the device at shift start
- Driver completes stops, captures signatures, and generates invoices with zero signal
- Auto-sync uploads completed data when a signal is detected
Impact: Zero downtime due to connectivity issues, 100% data integrity.
Component 3: Dispatch Control Center with ELD Integration
Custom software development solutions create dispatch platforms with:
Real-Time Fleet Visibility:
- Live map view with color-coded vehicle status
- Delivery progress indicators
- Performance metrics dashboard
- Exception alerts for delays/issues
Critical Integration: Hours of Service (HoS) Compliance
Modern routing engines integrate directly with Electronic Logging Devices (ELDs):
- Real-Time Constraint: Software sees Driver John has only 3.5 hours drive time remaining
- Auto-Adjustment: Automatically caps his route at 3 hours, moves excess stops to available drivers
- Result: 100% compliance with DOT regulations without manual calculation
This prevents violations that cost $1,000-$16,000 per incident and protects your operating authority.
Component 4: Precision Geofencing Technology
GPS gets drivers to the street address, but doesn’t show where the tank is. In industrial complexes or large farms, the fill pipe might be 500 yards from the front gate.
Polygon Geofence Solution:
Instead of simple “pin drops,” advanced systems use custom shapes drawn around exact fueling zones:
- Trigger Automation: Driver’s “Arrival” timestamp only triggers when the truck enters the polygon
- Billing Accuracy: Prevents disputes about waiting time
- Safety Routing: Guides the driver to a specific service entrance capable of handling hazmat tankers
Impact: 75% reduction in driver confusion, eliminates 90%+ of arrival time disputes, improves safety compliance.
Delivery Route Planning Software: Build vs. Buy vs. SaaS
Option 1: Off-the-Shelf Software
Best For: Small operations (1-5 vehicles), tight budgets, simple routing needs
Pros: Lower cost ($200-$800/month per vehicle), rapid deployment (2-6 weeks) Cons: Generic features, limited customization, and ongoing monthly costs
Option 2: Custom Development
Working with Custom software development solutions providers:
Best For: Mid-to-large operations (15+ vehicles), unique requirements, long-term strategic investment
Development Cost Breakdown:
| Component | Development Time | Cost Range |
| Routing Algorithm Core | 6-10 weeks | $35,000 – $75,000 |
| Mobile Driver App | 8-12 weeks | $40,000 – $95,000 |
| Dispatch Dashboard | 6-10 weeks | $30,000 – $70,000 |
| Integrations (ELD, Fuel Management) | 4-8 weeks | $20,000 – $45,000 |
| Testing & Deployment | 3-5 weeks | $15,000 – $35,000 |
| TOTAL | 27-45 weeks | $140,000 – $320,000 |
ROI Timeline: Positive ROI in 14-22 months for operations with 15+ vehicles.
Option 3: SaaS Platform (Recommended for Most)
SaaS application development services provide the middle ground:
Hybrid SaaS Approach:
- Core routing engine: Shared platform (cost-effective)
- Custom features: Tailored to fuel delivery specifics
- Modular pricing: Pay for features you need
- Rapid deployment: 4-8 weeks
Cost Structure:
- Setup/Onboarding: $5,000 – $25,000
- Monthly Subscription: $150 – $400 per vehicle
- Annual Cost (10 vehicles): $23,000 – $73,000
Best For: Most fuel delivery operations—optimal balance of cost, features, and flexibility.

Advanced Optimization Strategies
Strategy 1: Time-Based Dynamic Pricing
Offer delivery pricing that incentivizes customer flexibility:
| Delivery Option | Price | Route Impact | Customer Appeal |
| Scheduled (1-week advance) | Standard | Perfect optimization | Budget-conscious |
| Next-Day Delivery | +10% | Good optimization | Standard service |
| Same-Day Delivery | +25% | Moderate disruption | Convenience-focused |
| Emergency (4-hour) | +50% | Significant disruption | True emergencies |
Impact: Shifting 20-30% of deliveries to scheduled improves route efficiency by 12-18% while maintaining/increasing revenue.
Strategy 2: Collaborative Routing with Customers
Customer Portal Features:
- View available delivery time slots
- Select preferred windows (from optimized options)
- Reschedule flexibility when needed
- Track delivery approach in real-time
Benefits: Reduces failed deliveries by 85%+, improves optimization, increases satisfaction, and reduces customer service calls.
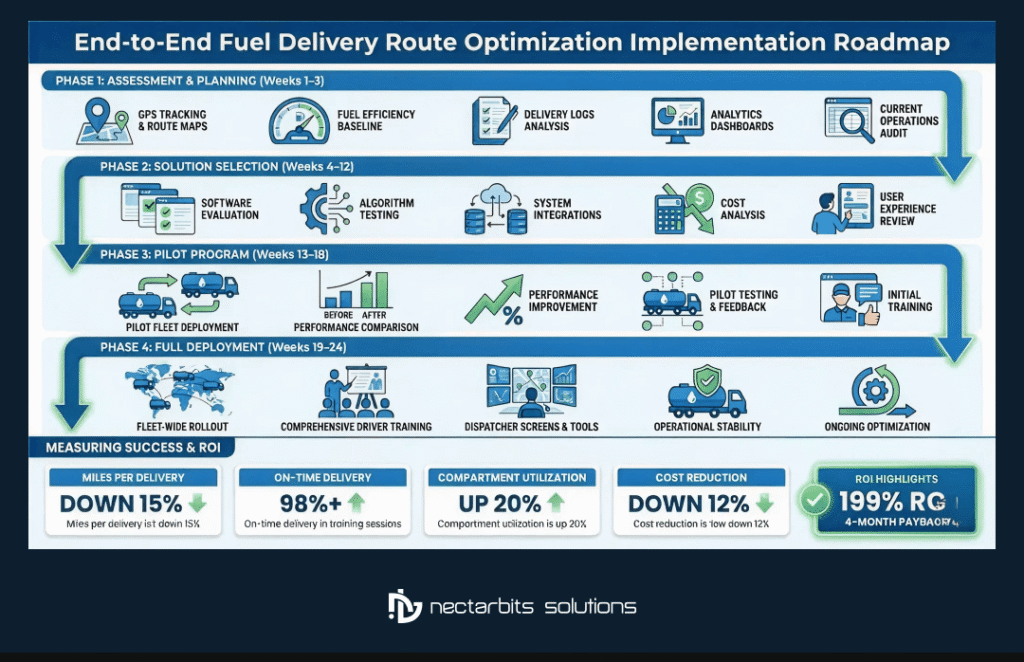
Implementation Roadmap
Phase 1: Assessment and Planning (Weeks 1-3)
Baseline Measurement:
| Metric | Measurement Method |
| Average Miles Per Route | GPS tracking data analysis |
| Deliveries Per Vehicle Per Day | Dispatch records review |
| Fuel Efficiency (MPG) | Fuel purchase vs. mileage data |
| On-Time Delivery % | Customer feedback + delivery logs |
| Compartment Return % | Fuel returned to base vs. capacity |
Phase 2: Solution Selection (Weeks 4-12)
Selection Criteria:
| Criterion | Weight | Evaluation Method |
| Fuel Delivery Expertise | 25% | Reference customers in fuel delivery |
| Algorithm Sophistication | 20% | Test with your actual routes |
| Integration Capability | 15% | Technical assessment with IT team |
| User Interface Quality | 15% | Driver and dispatcher testing |
| Total Cost of Ownership | 15% | 3-year cost projection |
Phase 3: Pilot Program (Weeks 13-18)
Select 2-3 vehicles for pilot, run parallel operations, compare daily performance, gather feedback, refine based on learning.
Pilot Success Metrics:
| Metric | Target Improvement | Minimum Acceptable |
| Miles Reduction | 20-30% | 15% |
| Deliveries Increase | 15-25% | 10% |
| Planning Time Reduction | 70-85% | 50% |
| Compartment Utilization | 90%+ | 85% |
Phase 4: Full Deployment (Weeks 19-24)
Vehicle-by-vehicle deployment with comprehensive training (2-3 hours per driver, full day for dispatchers).
Measuring Success: Key Performance Indicators
Operational Efficiency Metrics:
| KPI | Calculation | Target | Excellent |
| Miles Per Delivery | Total miles ÷ Deliveries | <15 miles | <12 miles |
| Deliveries Per Vehicle Day | Deliveries ÷ Vehicles ÷ Days | >12 | >15 |
| On-Time Delivery % | On-time deliveries ÷ Total | >93% | >97% |
| Compartment Utilization | Fuel delivered ÷ Capacity | >88% | >94% |
| Return Volume % | Fuel returned ÷ Capacity | <5% | <2% |
Financial Impact Metrics:
| Metric | 6-Month Target | 12-Month Target |
| Fuel Cost Per Delivery | -15% to -20% | -20% to -30% |
| Labor Cost Per Delivery | -12% to -18% | -18% to -25% |
| Total Cost Per Delivery | -18% to -25% | -25% to -35% |
| Revenue Per Vehicle | +12% to +18% | +18% to +25% |
ROI Calculation – 10 Vehicle Fleet Example
| Savings Category | Annual Amount |
| Fuel Savings (25% reduction) | $87,500 |
| Labor Savings (18% efficiency) | $94,500 |
| Maintenance Savings (20% reduction) | $24,000 |
| Vehicle Replacement Delay | $30,000 |
| Administrative Time Savings | $18,200 |
| TOTAL ANNUAL SAVINGS | $254,200 |
| Technology Investment (SaaS) | -$85,000 |
| NET YEAR 1 BENEFIT | $169,200 |
| ROI % | 199% |
| Payback Period | 4.0 months |
Read more about route optimization strategies, fuel cost reduction, and delivery efficiency best practices in our comprehensive guide to maximizing profitability.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Challenge 1: Driver Resistance to Technology
Solutions:
- Frame as driver benefit: “Easier routes, less stress, get home earlier.”
- Involve drivers in selection and testing
- Emphasize safety improvements
- Performance bonuses for adoption
- Gradual rollout with enthusiastic early adopters
Challenge 2: “Our Routes Are Already Optimal”
Reality: Manual routing achieves 60-75% of theoretical optimal efficiency at best.
Solution: Run a pilot comparison of algorithmic routes vs. actual historical routes. Typical discovery: 15-30% improvement potential even for “well-optimized” manual routes.
Challenge 3: System Integration Complexity
Work with developers who hire dedicated developers specializing in:
- API-based connections to fuel management systems
- Real-time data synchronization
- ELD integration for HoS compliance
- Robust error handling and fallback mechanisms
Future of Fuel Delivery Route Optimization
Emerging Technologies:
Autonomous Delivery Vehicles:
- Timeline: Limited deployment 2026-2028, broader adoption 2030+
- Impact: 24/7 operation, perfect route adherence, labor cost elimination
AI-Powered Predictive Ordering:
- Current: Customers order when low
- Future: AI predicts need, auto-generates orders, optimizes delivery timing
- Impact: Near-perfect route planning, minimal emergencies
Blockchain Route Verification:
- Application: Immutable delivery proof, automated smart contract payments
- Benefit: Eliminate billing disputes, instant payment processing
- Timeline: Early adoption 2025-2026

Conclusion: Driving Efficiency and Profitability
Optimizing fuel delivery routes is no longer optional—it’s essential for reducing costs, improving delivery capacity, and ensuring customer satisfaction. Advanced route planning strategies, including real-time rerouting, compartment-level load optimization, and predictive analytics, help fleets operate efficiently while minimizing waste and delays.
By adopting intelligent route optimization, fuel delivery companies can maximize operational performance, increase profitability, and turn logistics into a competitive advantage.
Related Resource:
Want to boost delivery performance beyond route planning? Advanced fleet routing and dispatch software uses real‑time data, AI optimization, and analytics to reduce fuel use, improve accuracy, and increase efficiency. Learn how intelligent fuel delivery dispatch solutions streamline operations and enhance fleet visibility.
Read more about intelligent fuel delivery dispatch solutions here
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How much improvement can we realistically expect?
Most fuel delivery operations achieve 20–35% cost reduction and 18–28% increase in delivery capacity within the first year. Typical gains include 25–40% fewer miles driven, 15–25% less time per delivery, and 20–30% more deliveries per vehicle.
Q2: How long does implementation take?
– SaaS solutions: 4–8 weeks from selection to full deployment
– Custom development: 6–9 months from requirements to full deployment
– Basic route optimization: Benefits can be realized in as little as 2–3 weeks
Q3: Will drivers accept the technology?
Driver acceptance ranges from 85–95% within 3 months when implemented effectively. Success factors include involving drivers in the selection process, emphasizing benefits like easier routes and reduced stress, providing thorough training, and starting with enthusiastic early adopters.
Q4: Can the optimization handle our unique constraints?
Yes—modern route optimization systems can manage:
– Hazmat routing restrictions
– Compartmentalized trucks with multiple fuel products
– Customer time windows and site access constraints
– Driver hours-of-service regulations
– Other fuel-specific delivery requirements
Q5: How do we handle emergency deliveries?
Advanced systems automatically identify the closest available vehicle, calculate the minimal disruption insertion point, reroute the affected vehicle, and communicate changes instantly to the driver. Emergency handling is integrated into the route optimization algorithms for seamless response.




