Quick Summary
The US–Canada fuel delivery market is a $450B opportunity, with $2.6B in petroleum trade per day. Navigating cross-border fuel delivery regulations requires DOT/EPA (US) and TDG/provincial permits (Canada), typically taking 4–6 months.
Key needs include hazmat-certified drivers, vehicle inspections, customs documentation, and environmental compliance.
Demand is strong across remote industries, agriculture, commercial fleets, and renewable fuels. Success depends on digital compliance tools, the FAST program, strategic partnerships, and $50K–$150K in insurance. Startup costs range $340–$1.09 M, mainly for trucks, permits, and technology.
The North American fuel transport market represents a $450 billion opportunity, with trade between the United States and Canada accounting for approximately $2.6 billion in petroleum products daily, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration. As fuel demand evolves and businesses seek more efficient distribution methods, cross-border fuel delivery operations are becoming increasingly strategic for companies aiming to expand their market reach.
However, navigating the complex landscape of international fuel delivery requires more than logistics planning.
From cross-border fuel delivery regulations to safety standards, customs procedures, and environmental requirements, companies must address multiple challenges to operate successfully across the US–Canada border. This guide explores the regulations, opportunities, and best practices for building profitable cross-border fuel operations.
Understanding the Cross-Border Fuel Delivery Landscape
Market Overview and Trade Dynamics
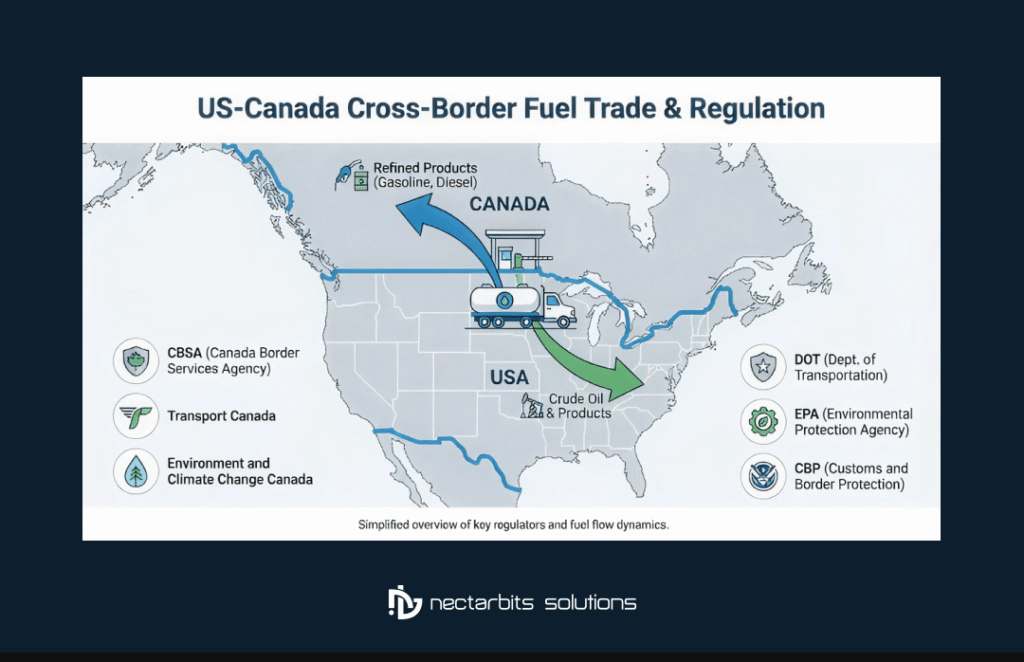
The United States and Canada share the world’s longest international border, spanning approximately 5,525 miles. This proximity, combined with integrated economies and complementary energy markets, creates unique opportunities for fuel distribution companies. Canada exports substantial volumes of crude oil to the United States while importing refined petroleum products, creating a continuous flow of energy products across the border.
The cross-border fuel delivery market encompasses several key segments:
- Commercial fleet fueling services
- Industrial and agricultural fuel supply
- Emergency fuel delivery operations
- Retail fuel distribution
- Specialized fuel products for mining and construction
Key Regulatory Bodies
Multiple agencies govern cross-border fuel delivery regulations on both sides of the border:
United States:
- Department of Transportation (DOT) Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
- Customs and Border Protection (CBP)
- Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA)
Canada:
- Transport Canada
- Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA)
- Environment and Climate Change Canada
- Provincial transportation ministries
Each agency maintains specific requirements that transport companies must satisfy to operate legally and safely across international boundaries.
Essential Permits and Licenses for Cross-Border Operations
US Requirements
Companies engaged in cross-border fuel delivery must obtain several critical permits before commencing operations. The DOT requires hazardous materials transportation permits for vehicles carrying fuel products, including detailed documentation of vehicle specifications, safety equipment, and driver qualifications. In some cases, partnering with a custom software development company USA can help streamline compliance tracking and documentation workflows.
The EPA mandates registration for any entity importing or exporting petroleum products. Companies must demonstrate full compliance with fuel quality standards and environmental regulations applicable to both jurisdictions.
Canadian Requirements
Canadian operations require parallel documentation and certification. Transport Canada issues Transportation of Dangerous Goods (TDG) certificates for drivers and companies handling hazardous materials. These certifications involve comprehensive training on safety procedures, emergency response, and proper documentation practices.
Provincial requirements vary significantly across Canada. Companies must research and comply with specific regulations in each province where they plan to operate, including provincial fuel tax collection and remittance requirements.
The CBSA administers customs procedures for goods entering Canada, including petroleum products. Importers must register for a business number and may need to post security bonds depending on the volume and frequency of shipments.
Application Process Timeline
| Permit Type | Jurisdiction | Processing Time | Renewal Period |
| DOT Hazmat Permit | United States | 60-90 days | Annual |
| EPA Registration | United States | 30-45 days | Annual |
| USDOT Number | United States | 10-20 days | Biennial Update |
| TDG Certificate | Canada | 30-60 days | 3 Years |
| Provincial Permits | Canada (varies) | 30-90 days | Annual to 3 Years |
| CBSA Business Number | Canada | 15-30 days | Permanent |
Planning is essential, as the complete permitting process can take four to six months for new operations.
Safety Standards and Compliance Requirements
Vehicle and Equipment Standards
Both countries enforce rigorous safety standards for fuel transport vehicles. Tanks must meet specific design, construction, and testing requirements outlined in DOT and Transport Canada regulations. Regular inspections verify structural integrity, proper labeling, emergency equipment, and leak prevention systems.
Safety equipment requirements include fire extinguishers, spill containment materials, emergency response information, and communication devices. Vehicles must display proper placarding identifying the hazardous materials being transported, following international standards for dangerous goods identification.
Driver Qualifications and Training
Drivers conducting international fuel delivery must meet qualification standards in both countries. This includes possessing appropriate commercial driver’s licenses with hazardous materials endorsements, completing TDG training for Canadian operations, and maintaining clean driving records.
Companies must implement comprehensive driver training programs covering border crossing procedures, customs documentation, emergency response protocols, and regulatory compliance. Regular refresher training ensures drivers stay current with evolving regulations.
Documentation and Record-Keeping
Proper documentation is critical for cross-border fuel delivery operations. Required documents include bills of lading, shipping papers with emergency response information, customs declarations, fuel quality certificates, and tax documentation for both jurisdictions.
Companies must maintain detailed records of all shipments, including origin and destination information, product specifications, quantities, driver information, and vehicle details. These records must be readily accessible for inspection by regulatory authorities and typically must be retained for three to seven years, depending on the specific regulation.

Customs and Border Procedures
Pre-Clearance Programs
Expedited border crossing programs significantly improve operational efficiency for international fuel delivery. The Free and Secure Trade (FAST) program allows pre-approved, low-risk shipments to cross the border more quickly through dedicated lanes and reduced documentation requirements.
Some companies also work with a cross-platform app development company in Toronto to build custom solutions that streamline compliance tracking and border documentation.
Documentation Requirements
Complete and accurate documentation is essential for smooth border crossings. The customs declaration must include detailed product information, harmonized tariff codes, country of origin, shipper and consignee details, and the commercial value of the shipment.
Electronic data submission through systems like the Automated Commercial Environment (ACE) in the United States or the Canadian Single Window initiative streamlines the declaration process and reduces delays at physical border crossings.
Inspection Procedures
Border officials may conduct physical inspections of fuel transport vehicles to verify documentation accuracy, confirm product specifications, check for safety compliance, and screen for security threats. While participating in trusted trader programs reduces inspection frequency, companies must always be prepared for potential examinations.
Environmental Regulations and Sustainability Requirements
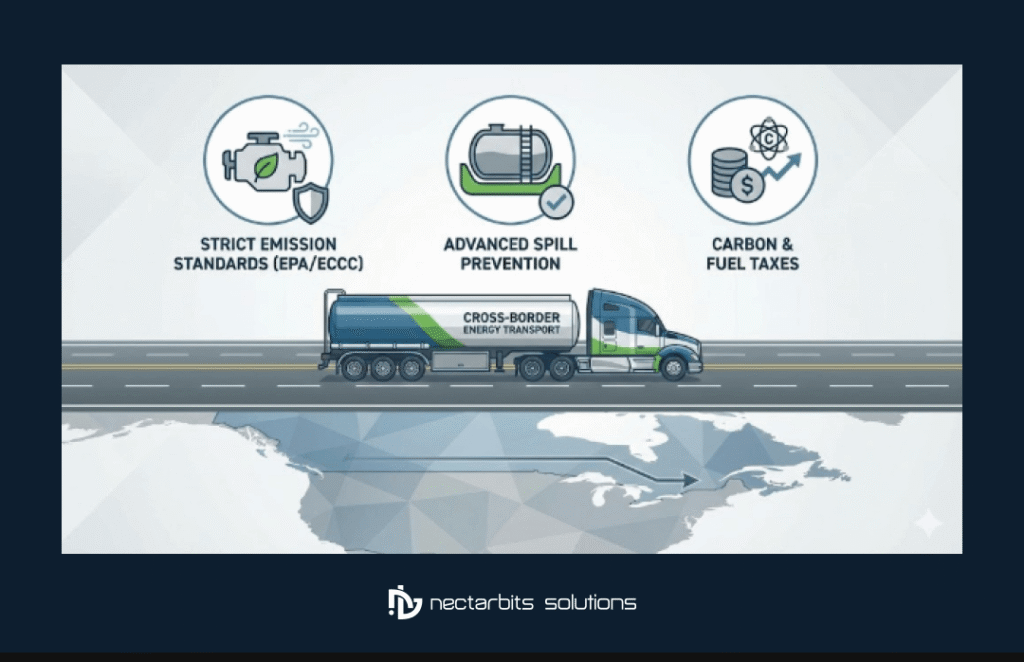
Emission Standards
Both countries enforce progressively stricter emission standards for transport vehicles. The EPA’s greenhouse gas emissions standards for heavy-duty vehicles align closely with Canadian requirements, but companies must verify compliance in both jurisdictions.
Newer vehicles meeting current emission standards face fewer operational restrictions and benefit from more favorable regulatory treatment. Many jurisdictions offer incentives for fleets that exceed minimum requirements or adopt alternative fuel technologies.
Spill Prevention and Response
Comprehensive spill prevention, control, and countermeasure plans are mandatory for fuel transport operations. These plans must detail preventive measures to minimize spill risks, containment procedures if spills occur, notification protocols for environmental agencies, and cleanup and remediation procedures.
Companies must conduct regular training and drills to ensure personnel can execute emergency response plans effectively. Equipment for spill containment must be readily accessible on all transport vehicles and at storage facilities.
Carbon Pricing and Fuel Taxes
Canada’s federal carbon pricing system and various provincial carbon tax regimes affect the economics of fuel transport. Companies must understand applicable carbon costs and build these into pricing structures. Some jurisdictions offer exemptions or reduced rates for certain fuel types or uses.
Similarly, fuel tax requirements differ between jurisdictions. Companies engaged in cross-border fuel delivery must track tax obligations carefully, remit appropriate taxes, and maintain documentation proving tax compliance to avoid penalties.
Technology Solutions for Cross-Border Fuel Delivery
Fleet Management Systems
Modern fleet management technology provides critical capabilities for international fuel delivery operations. GPS tracking enables real-time location monitoring, route optimization reduces transit times and costs, and automated compliance reporting simplifies regulatory adherence.
Advanced systems integrate with customs platforms, automatically generate required documentation, and provide predictive analytics to optimize operations. These capabilities become particularly valuable when managing complex cross-border logistics involving multiple jurisdictions with varying requirements.
Digital Documentation Platforms
Paper-based documentation creates risks of errors, delays, and compliance failures. Digital platforms centralize document management, automate data entry from multiple sources, ensure consistency across required forms, and provide secure storage with easy retrieval.
Electronic systems facilitate information sharing between drivers, dispatchers, customers, and regulatory authorities, reducing communication delays and improving operational transparency.
Mobile Applications for Drivers
Driver-facing mobile applications transform the delivery experience by providing turn-by-turn navigation optimized for commercial vehicles, real-time border wait time information, electronic document capture and submission, and immediate access to emergency response information.
Mobile technology also enables better communication between drivers and operations teams, allowing quick resolution of issues and real-time updates to customers regarding delivery status.
Explore how on-demand fuel delivery apps are transforming fleet fueling — Read the full Filld Case Study →
Insurance and Liability Considerations
Required Coverage Types
Cross-border fuel delivery operations require comprehensive insurance coverage addressing both countries’ requirements. Commercial auto liability insurance must meet or exceed minimum limits in both jurisdictions, with many companies maintaining coverage well above legal minimums to protect against catastrophic claims.
Cargo insurance protects against loss or damage to fuel products during transport. Environmental liability coverage addresses cleanup costs and third-party claims resulting from spills or contamination. Companies should also consider business interruption insurance to mitigate financial impacts from operational disruptions.
International Coverage Requirements
Standard insurance policies may not provide adequate coverage for international operations. Companies must verify that their policies explicitly cover cross-border activities and meet requirements in both the United States and Canada.
Working with insurers experienced in international transportation ensures an appropriate coverage structure and helps navigate differences in legal frameworks between countries. Some insurers specialize in North American transportation and offer policies specifically designed for cross-border operations.
Market Opportunities and Growth Strategies
Emerging Market Segments
The cross-border fuel delivery market continues to evolve, creating new opportunities for forward-thinking companies. Remote work sites in mining, forestry, and construction increasingly rely on delivered fuel rather than maintaining on-site storage.
Agricultural operations require reliable fuel delivery during critical planting and harvest periods. The shift toward renewable fuels opens avenues for specialized products like biodiesel, renewable diesel, and sustainable aviation fuel, which often command premium pricing and face less competition.
Companies can also leverage digital tools to optimize delivery, track operations, and enhance customer experience-explore our mobile app development solutions → to support these initiatives.
Strategic Partnerships
Successful cross-border operations often involve strategic partnerships that extend market reach and operational capabilities. Partnering with established fuel suppliers in each country provides access to reliable product sources, relationships with local distributors and retailers, and knowledge of regional market conditions.
Technology partnerships enable companies to deploy sophisticated systems without massive capital investments. Collaborating with logistics providers offering complementary services creates opportunities for bundled offerings that provide greater customer value.
Competitive Advantages
Companies that excel in cross-border fuel delivery typically differentiate themselves through superior reliability and on-time performance, proactive communication with customers, competitive pricing enabled by operational efficiency, and comprehensive service offerings addressing diverse customer needs.
Investing in technology, training, and process optimization creates sustainable competitive advantages that are difficult for competitors to replicate quickly.
Risk Management and Contingency Planning
Regulatory Risk Mitigation
Regulations governing international fuel delivery change periodically, creating compliance risks for unprepared companies. Establishing a robust regulatory monitoring program ensures awareness of pending changes, adequate preparation time for compliance updates, and proactive rather than reactive postures toward new requirements.
Engaging regulatory consultants or legal counsel with expertise in transportation law provides valuable guidance on complex or ambiguous requirements and helps navigate enforcement actions if violations occur.
Operational Disruptions
Border closures, weather events, equipment failures, and other disruptions can severely impact cross-border fuel delivery operations. Comprehensive contingency plans address alternative routing options when primary border crossings are unavailable, backup equipment and vehicle capacity, relationships with third-party carriers for emergency capacity, and communication protocols for customer notification.
Companies should regularly test contingency plans through exercises that simulate realistic disruption scenarios, identifying weaknesses and areas for improvement before actual emergencies occur.
Financial Risk Management
Currency exchange rate fluctuations can significantly impact profitability for cross-border operations. Companies should implement hedging strategies to manage currency risk, price contracts appropriately to reflect exchange rate volatility, and maintain banking relationships in both countries to facilitate transactions.
Careful credit management and payment terms help minimize exposure to customer defaults, particularly when extending credit across international boundaries, where collection may be more challenging.

Best Practices for Successful Cross-Border Operations
Pre-Operational Planning
Companies entering the cross-border fuel delivery market should invest substantial time in planning before commencing operations. This includes conducting comprehensive market research to understand demand, competition, and pricing dynamics, developing detailed financial projections incorporating all regulatory and operational costs, and establishing relationships with suppliers, customers, and service providers.
Thorough preparation significantly reduces the risk of costly mistakes and operational failures during the critical startup phase.
Compliance Management Systems
Maintaining compliance across multiple jurisdictions requires systematic approaches rather than ad hoc efforts. Successful companies implement compliance management systems featuring centralized tracking of permit renewals and regulatory deadlines, standardized processes for documentation and record-keeping, and regular internal audits to verify ongoing compliance.
Investing in fuel delivery app development can also help automate tracking, improve documentation accuracy, and ensure regulatory adherence. Continuous training programs for drivers and operational staff further strengthen compliance.
Continuous Improvement Culture
The most successful cross-border fuel delivery operations embrace continuous improvement philosophies. Regularly analyzing operational data to identify efficiency opportunities, soliciting feedback from drivers and customers, benchmarking performance against industry standards, and investing in technology and process upgrades create competitive advantages that compound over time.
Companies that view their operations as continually evolving rather than static are better positioned to adapt to market changes and capitalize on new opportunities.
Financial Considerations and Cost Analysis
Startup Costs
Entering the cross-border fuel delivery market requires significant capital investment. Major cost categories include vehicle and equipment acquisition, permits and licensing fees, insurance premiums, technology systems implementation, initial inventory investment, and working capital for accounts receivable.
| Cost Category | Estimated Range (USD) |
| Vehicle/Equipment (per unit) | $150,000 – $300,000 |
| Initial Permits/Licenses | $15,000 – $40,000 |
| Annual Insurance | $50,000 – $150,000 |
| Technology Systems | $25,000 – $100,000 |
| Working Capital | $100,000 – $500,000 |
Companies should develop detailed financial models incorporating all startup costs and conservative revenue projections to ensure adequate capitalization.
Ongoing Operational Costs
Beyond startup investments, cross-border fuel delivery operations incur substantial ongoing costs, including fuel and vehicle maintenance, driver salaries and benefits, permit renewals and compliance costs, insurance premiums, and technology subscription and maintenance fees.
Understanding the complete cost structure enables accurate pricing decisions and realistic profitability expectations.
Revenue Optimization
Maximizing revenue requires strategic approaches to pricing, customer acquisition, and service delivery. Dynamic pricing models that reflect supply and demand fluctuations, fuel cost pass-through mechanisms protecting margins from commodity price volatility, and premium pricing for expedited or specialized services help optimize revenue.
Building long-term contracts with creditworthy customers provides revenue stability and improves cash flow predictability, supporting sustainable growth.
Want to dig deeper? Read our full financial analysis and case study on cost structure and profitability → Fuelster App Case Study: Premium Fuel Delivery Service
Future Trends in Cross-Border Fuel Delivery
Regulatory Evolution
Regulatory frameworks continue to evolve in response to environmental priorities, safety innovations, and economic factors. Companies should anticipate increasingly stringent emission standards driving fleet upgrades, enhanced safety requirements incorporating new technologies, streamlined customs procedures leveraging digital systems, and harmonized standards between the United States and Canada.
Staying ahead of regulatory trends positions companies to adapt quickly and potentially gain competitive advantages through early adoption of new requirements.
Technology Advancement
Emerging technologies promise to transform cross-border fuel delivery operations significantly. Autonomous vehicle technology may eventually reduce driver costs and extend operational hours. Blockchain-based documentation systems could revolutionize customs and compliance processes. Advanced analytics and artificial intelligence will enable increasingly sophisticated route optimization and demand forecasting.
Companies that thoughtfully adopt new technologies while managing implementation risks will lead the industry’s evolution.
Market Transformation
The broader energy transition toward lower-carbon fuels will reshape the cross-border fuel delivery market. Demand for renewable diesel, sustainable aviation fuel, and hydrogen will grow substantially, requiring new handling capabilities and supply chains. Companies positioning themselves to serve these emerging markets while maintaining traditional fuel delivery capabilities will capture significant growth opportunities.

Conclusion
Cross-border fuel delivery between the US and Canada offers strong growth potential for companies that can manage regulatory complexity, invest in the right technology, and run safe, efficient operations. Success depends on strict compliance with cross-border fuel delivery regulations, solid safety and environmental systems, smart use of digital tools, and strategic partnerships. With careful planning, expert guidance, and a commitment to quality, businesses can overcome entry barriers and tap into a high-value North American fuel transport market.
Take the Next Step in Cross-Border Fuel Delivery
Ready to expand your fuel delivery operations across the US-Canada border? Whether you’re launching new cross-border services or optimizing existing operations, having the right technology infrastructure is essential for regulatory compliance and operational efficiency.
Our team specializes in building custom software solutions that streamline international fuel logistics, automate compliance reporting, and improve customer satisfaction. From fleet management systems to mobile driver applications, we create technology that powers successful cross-border operations.
Continue Learning:
As fuel delivery operations grow more complex, leveraging enterprise-grade software solutions is key to efficiency, scalability, and compliance. Companies can transform their processes, optimize resource management, and enhance customer experiences through tailored digital platforms.
To explore how top-tier enterprise software can drive innovation and operational excellence, check out our detailed guide: NectarBits: Top Enterprise Software Development Company. This resource highlights best practices, emerging technologies, and strategies for building robust, scalable systems across industries.
FAQs:
1. What permits are needed for cross-border fuel delivery between the US and Canada?
US requirements include DOT hazmat permits, EPA registration, and a USDOT number. In Canada, TDG certificates, provincial permits, and a CBSA business number are needed. Processing can take 15–90 days, so plan.
2. How can companies ensure safety and environmental compliance?
Maintain proper vehicle inspections, driver training, placarding, and documentation. Follow emission standards, spill prevention plans, and carbon tax rules. Digital fleet management and fuel delivery apps simplify compliance.
3. How can companies reduce border delays in fuel delivery?
Use FAST or other pre-clearance programs, ensure accurate digital documentation, and partner with local suppliers or logistics providers to streamline operations.
4. What are the key opportunities and trends in US–Canada fuel transport?
Demand is growing in remote industries and renewable fuels. Technologies like AI route optimization, autonomous vehicles, and blockchain for compliance are transforming operations.




